
The holder in due course will have a greater right to payment because the maker or payor cannot assert certain defenses (personal defenses) to payment against the holder in due course.Įxample: In the above scenario, suppose Robert provides Sarah with a negotiable promissory note.
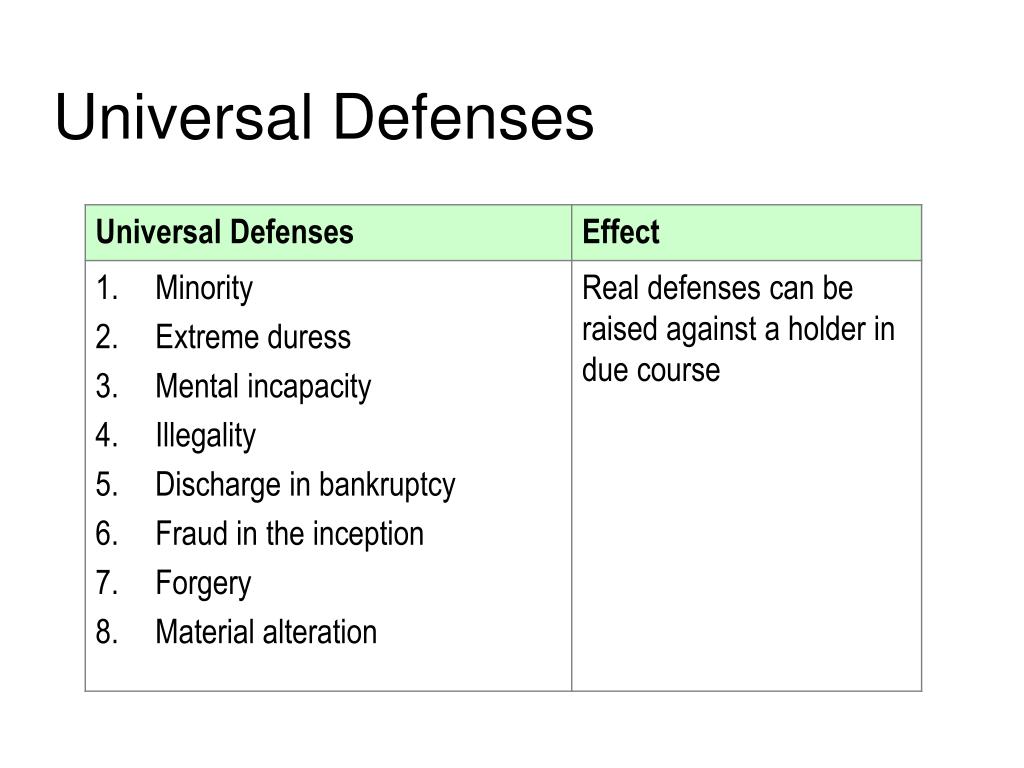
That is, when paper is negotiable and validly negotiated to a subsequent holder who qualifies as a holder in due course, the holder may acquire greater rights to enforce the instrument against the payor or maker. The holder of negotiable paper may have greater rights than the original issuee. This possibility makes the note far less valuable to Tim. If Robert has a defense against his obligation to pay Sarah for the equipment (e.g., the equipment is faulty), he could assert that defense against his obligation to pay Tim if he presents the promissory note for payment. She transfers the note to Tim, who is now the holder. So, Sarah is the holder of a promissory note that is non-negotiable. Robert gives Sarah a non-negotiable promissory note to pay for the goods. As such, the value of non-negotiable instrument is far less valuable to a subsequent transferee who cannot be certain that she will receive payment without being subject to a payor defense.Įxample: Sarah enters into a contract to sell equipment to Robert. This means that, if the original party loses his right to be paid (think of defenses to payment of a contract), so does the transferee of the commercial paper. That is, she has the exact same rights in the instrument as the original issuee held. The rights of a holder of each type of paper is as follows: What is Non-negotiable Commercial Paper?Īn individual in possession of a non-negotiable instrument stands in the shoes of the original issuee. Next Article: Requirements for Commercial Paper to be Negotiable Back to: COMMERCIAL PAPER What are the Characteristics of Commercial Paper? This is because the holder has fewer rights in enforcing payment of the non-negotiable, commercial paper.

Paper that is not negotiable may still be transferred however, it is far less valuable than negotiable paper. Negotiability concerns the rights of the holder of commercial paper. To be a substitute for money, commercial paper must be freely transferable in the marketplace. Negotiation is the transfer of negotiable paper from one holder to another. This is known as Bridge Financing.Update Table of Contents What is negotiability and why is it important? What are the Characteristics of Commercial Paper? What is Non-negotiable Commercial Paper? What is Negotiable Commercial Paper? Discussion Question Practice Question Academic Research What is negotiability and why is it important? Funds raised through commercial paper are used to meet the floatation costs. In order to raise the long-term funds in the capital market, the company will have to incur floatation costs (costs associated with the floating of an issue are brokerage, commission and advertising etc.). For example, companies use this instrument for purposes such as bridge financing.Įxample: Suppose a company needs long-term finance to buy some equipment. The original purpose of the commercial paper was to provide short-term funds for seasonal and working capital needs. It is sold at a discount and redeemed at par. The issuance of commercial paper is an alternative to bank borrowing for large companies that are generally considered to be financially strong. Commercial paper is generally issued at a discount from face value and reflects prevailing market interest rates. Maturities on commercial paper hardly ever range any longer than 270 days. It is issued by large and creditworthy companies to raise short-term funds at lower rates of interest than market rates.

Commercial paper is a short-term unsecured promissory note, negotiable and transferable by endorsement and delivery with a fixed maturity period.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
